Research
Our research aims are to characterise the genetics and molecular mechanisms of B and T-cell lymphomas and to improve their diagnosis, prognosis and treatment stratifications. We have a longstanding research interest in extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT lymphoma), splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL), follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL). We use a range of conventional and state-of-the-art technologies including DNA/RNA in situ hybridisation, DNA and RNA sequencing, and various in vitro assays to profile somatic genetic changes, and investigate how genetic alterations cooperate with immunological drive in lymphoma development. We also actively translate research findings into routine clinical practice, improving diagnosis, prognostication and treatment stratification.
We are a part of the UK national consortium of Precision Medicine in Aggressive Lymphoma (PMAL), contributing genomic profiling to a range of clinical trials on lymphoma.
Group members
Zi Chen, Research Associate
Ewelina Madej, Research Associate
Maria-Myrsini Tzioni, PhD student
Jingwen Xu, PhD student
Keying Chen, MPhil Student
Fang Guo, visiting pathologist
Lulwa Al Shamari, visiting pathologist
Publications
MALT lymphoma
Liu H, Ye H, Ruskone-Fourmestraux A, De Jong D, Pileri S, Thiede C, Lavergne A, Boot H, Caletti G, Wundisch T, Molina T, Taal BG, Elena S, Thomas T, Zinzani PL, Neubauer A, Stolte M, Hamoudi RA, Dogan A, Isaacson PG, Du MQ. T(11;18) is a marker for all stage gastric MALT lymphomas that will not respond to H. pylori eradication. Gastroenterology 2002;122:1286-94.
Rosebeck S, Madden L, Jin X, Gu S, Apel IJ, Appert A, Hamoudi RA, Noels H, Sagaert X, Van Loo P, Baens M,Du MQ, Lucas PC, McAllister-Lucas LM. Cleavage of NIK by the API2-MALT1 fusion oncoprotein leads to noncanonical NF-kappaB activation. Science2011, 331:468-72.
Hamoudi RA, Appert A, Ye H, Ruskone-Fourmestraux A, Streubel B, Chott A, Raderer M, Gong L, Wlodarska I, De Wolf-Peeters C, MacLennan KA, de Leval L, Isaacson PG, Du MQ. Differential Expression of NF-kB target genes in MALT lymphoma with and without chromosome translocation: insights into molecular mechanism. Leukaemia2010;24:1487-97.
Moody S, Thompson JS,Chuang SS, Liu H, Raderer M,Vassiliou G, Wlodarska I,Wu F,Cogliatti S, Robson A, Ashton-Key M, Bi Y, Goodlad J,Du MQ.Novel GPR34 and CCR6 mutation, and distinct genetic profiles in MALT lymphomas of different sites.Haematologica2018; 103 (8): 1329-1336. (Accompanied by editorial comments)
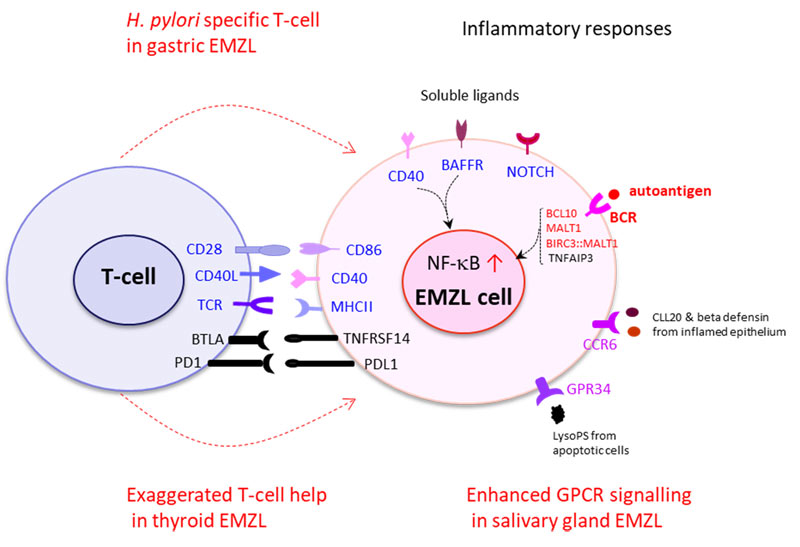
Wu F, Watanabe N, Tzioni MM, Akarca A, Zhang C, Li Y, Chen Z, Cucco F, Carmell N, Noh JY, Ito K, Dobson R, Moody S, Yao W, Zhang W, Liu W, Liu H, Okosun J, Chott A, Bi Y, Chuang SS, Raderer M, Li JY, Marafioti T, Du MQ. Thyroid MALT lymphoma: self-harm to gain T-cell help. Leukemia 2021 35(12):3497-3508.
Korona B, Korona D, Wotherspoon AC, Du MQ. GPR34 activation bridges lymphoepithelial lesion to genesis of salivary gland MALT lymphoma. Blood. 2022:139(14):2186-2197.
Korona B, Korona D, Zhao W, Wotherspoon AC, Du MQ. CCR6 activation links innate immune responses to MALT lymphoma development. Haematologica 2022;107(6):1384-1396.
Tzioni MM, Watanabe N, Chen Zi, Wu F, Madej E, Makker J, Guo S, Attygalle AD, Wotherspoon A, Sugino K, Ito K, Du MQ. Primary thyroid B-cell lymphoma: molecular insights of its clonal evolution and relapse. J Pathol 2025; 265(2): 123-131.
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Clipson A, Wang M, de Leval L, Ashton-Key M, Wotherspoon A, Vasilliou G, Bolli N, Grove C, Moody S, Escudero-Ibarz L, Gundem G, Brugger K, Xue X, Mi E, Bench A, Scott M, Liu H, Follows G, Robles EF, Martinez Climent JA, Oscier D, Watkins AJ, Du MQ. KLF2mutation is the most frequent somatic change in splenic marginal zone lymphoma and identifies a subset with distinct genotype. Leukemia 2015; 29: 1177-85.
Follicular lymphoma
Dobson R, Wotherspoon A, Liu S, Cucco F, Chen Zi, Tang Y, Du MQ. Widespread in situ follicular neoplasia in patients who subsequently developed follicular lymphoma. J Pathol 2022 Apr;256(4):369-377.
Tzioni MM, Wotherspoon A, Chen Z, Cucco F, Makker J, Du MQ. Divergent evolution of metachronous follicular lymphoma and extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue from a common precursor. J Pathol. 2023 Sep;261(1):11-18.
Makker J, Wotherspoon A, Tzioni MM, Chen Z, Guo S, Cucco F, Du MQ. Majority of relapses in early-stage follicular lymphoma develop via a divergent evolution from their common precursor. Journal of Pathology (Accepted)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Sha C*, Barrans S*, Cucco F*, Bentley MA, Care MA, Cummin T, Kennedy H, Thompson JS, Uddin R, Worrillow L, Chalkley R, van Hoppe M, Ahmed S, Maishman T, Caddy J, Schuh A, Marmot C, Burton C , Tooze R, Davies A, Du MQ**, Johnson PWM**, Westhead DR**.Molecular definition of high grade B cell lymphoma: a centroblast-like group with potential for more effective therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2018 Dec 3:JCO1801314. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01314.*Equal first author; **Equal senior author. (Accompanied by editorial comments)
Davies A, Cummin T, Barrans S, Maishman T, Mamot C, Novak U, Caddy J, Kazmi-Stokes S, McMillan A, Fields P, Pocock C, Collins G, Cucco F, Sha C, Tooze R, Care M, Griffiths G, Du MQ, Westhead D, Burton C, Johnson P. Gene expression profiling in an open-label randomised, phase 3 trial (REMoDL-B) of bortezomib added to standard chemoimmunotherapy for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Lancet Oncology 2019; 20:649-662.
Cucco F, Barrans S, Sha C, Clipson A, Crouch S, Dobson R, Chen Z, Thompson JS, Care MA, Cummin T, Caddy J, Liu H, Robinson A, Schuh A, Fitzgibbon J, Painter D, Smith A, Roman E, Tooze R, Burton C, Davies AJ, Westhead DR, Johnson PWM, Du MQ. Distinct genetic changes reveal evolutionary history and heterogeneous molecular grade of DLBCL with MYC/BCL2 double-hit. Leukemia 2020; 34:1329-41
Davies A, Barrans S, Stanton L, Caddy J, Wilding S, Saunders G, Mamot C, Novak U, McMillan A, Fields P, Pocock C, Collins GP, Stephens R, Cucco F, Sha C, van Hoppe M, Tooze R, Care MA, Griffiths G, Schuh A, Burton C, Westhead DR, Du MQ, Johnson PWM. Differential efficacy from the addition of bortezomib to R-CHOP in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma according to molecular subgroup in the REMoDL-B study with 5 years follow up. J Clin Oncol. 2023 May 20;41(15):2718-2723.
Zhang C, Stelloo E, Barrans S, Cucco F, Jiang D, Tzioni1 MM, Chen Z, Li Y, Rásó-Barnett L, Liu L, El-Daly H, Soilleux E, Shah N, Nagumantry SK, Kyaw M, Prahladan MP, Tooze R, Westhead DR, Feitsma H, Davies AJ, Burton C, Johnson PWM, Du MQ. Non-IG::MYC in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma confers variable genomic configurations and MYC transactivation potential. Research Gate DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3388682/v1
Davies A, Barrans S, Stanton L, Caddy J, Wilding S, Saunders G, Mamot C, Novak U, McMillan A, Fields P, Pocock C, Collins GP, Stephens R, Cucco F, Sha C, van Hoppe M, Tooze R, Care MA, Griffiths G, Schuh A, Burton C, Westhead DR, Du MQ, Johnson PWM. Differential efficacy from the addition of bortezomib to R-CHOP in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma according to molecular subgroup in the REMoDL-B study with 5 years follow up. J Clin Oncol. 2023 May 20;41(15):2718-2723
T-cell lymphoma
Yao WQ, Wu F, Zhang W, Chuang SS, Thompson JS, Chen Z, Zhang SW, Clipson A, Wang M, Liu H, Bibawi H, Huang Y, Campos L, Grant JW, Wright P, EI-Daly H, Rásó-Barnett L, Farkas L, Follows GA, Gao Z, Attygalle AD, Ashton-Key M, Liu W, Du MQ. Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma contains multiple clonal T-cell populations derived from a common TET2 mutant progenitor cell. Journal of Pathology 2020; 250:346-357.
Dobson R, Du PY, Rásó-Barnett L, Yao WQ, Chen Zi, Casa C, EI-Daly H, Farkas L, Soilleux E, Wright P, Grant JW, Rodriguez-Justo M, Follows GA, Rashed H, Wotherspoon A, Attygalle AD, Liu H, Du MQ. Early detection of T-cell lymphoma with T follicular helper phenotype by RHOA mutation analysis. Haematologica. 2022;107(2):489-499.
Attygalle AD, Dobson R, Chak PK, Vroobel KM, Wren D, Kaur M, Ahmad R, ChenZ, Naresh KN, Du MQ. Parallel evolution of two distinct lymphoid neoplasms in clonal haematopoiesis. Histopathology 2022 Apr;80(5):847-858. doi: 10.1111/his.14619.
Molecular pathology and diagnosis
Liu H, Brais R, Lavergne-Slove A, Zeng Q, Payne K, Ye H, Liu Z, Carreras J, Huang Y, Bacon CM, Save V, Venkatraman L, Isaacson PG, Woodward J, Du MQ. Continual Monitoring of Intraepithelial Lymphocyte Immunophenotype and Clonality Is More Important Than Snapshot Analysis in the Surveillance of Refractory Coeliac Disease. Gut 2010; 59:452-60.
Cucco F,* Clipson A,* Kennedy H, Thompson JS, Wang M, Barrans S, van Hoppe M, Ochoa Ruiz E, Caddy J, Hamid D, Cummin T, Burton C, Davies AJ, Johnson P, Du MQ. Mutation Screening Using Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues: A Stratified Approach According to DNA Quality. Laboratory Investigation 2018; 98:1084-92. *Equal first author;
Reviews
Isaacson PG, Du MQ. MALT lymphoma: from morphology to molecule. Nature Review Cancer 2004; 4:644-53.
Du MQ. MALT lymphoma: a paradigm of NF-B deregulation. Seminars in Cancer Biology. 2016;39:49-60.
Alaggio R, Amador C, Anagnostopoulos I, Attygalle AD, Araujo IBO, Berti E, Bhagat G, Borges AM, Boyer D, Calaminici M, Chadburn A, Chan JKC, Cheuk W, Chng WJ, Choi JK, Chuang SS, Coupland SE, Czader M, Dave SS, de Jong D, Du MQ,* Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Ferry J*, Geyer J, Gratzinger D, Guitart J, Gujral S, Harris M, Harrison CJ, Hartmann S, Hochhaus A, Jansen PM, Karube K, Kempf W, Khoury J, Kimura H, Klapper W, Kovach AE, Kumar S, Lazar AJ, Lazzi S, Leoncini L, Leung N, Leventaki V, Li XQ, Lim MS, Liu WP, Louissaint A Jr, Marcogliese A, Medeiros LJ, Michal M, Miranda RN, Mitteldorf C, Montes-Moreno S, Morice W, Nardi V, Naresh KN, Natkunam Y, Ng SB, Oschlies I, Ott G*, Parrens M, Pulitzer M, Rajkumar SV, Rawstron AC, Rech K, Rosenwald A, Said J, Sarkozy C, Sayed S, Saygin C, Schuh A, Sewell W, Siebert R*, Sohani AR, Tooze R, Traverse-Glehen A, Vega F, Vergier B, Wechalekar AD, Wood B, Xerri L, Xiao W. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1720-1748, * correspondence author (authors arranged alphabetically according to surname)
Coupland SE, Du MQ*, Ferry JA, de Jong D, Khoury JD, Leoncini L, Naresh KN, Ott G, Siebert R, Xerri L, on behalf of the WHO 5th Edition Classification Project. the 5th edition of the WHO classification of mature B-cell neoplasms: open questions for research. Journal of Pathology 2024; 262(3):255-270. doi: 10.1002/path.6246. *Corresponding author
Du MQ. EMZL at various sites: learning from each other. Blood. 2025 Feb 5:blood.2024025794. doi: 10.1182/blood.2024025794. Online ahead of print.